이진 탐색 트리(Binary Search Tree)
각각의 노드가 최대 2개의 자식(Child) 노드를 가질 수 있는 트리 구조 중 하나이다. 이진 탐색 트리는 index 검색이나 숫자들을 비교하는 작업을 수행할 경우 좋은 성능을 보인다.
- 루트(Root) 노드를 기준으로 작은 값은 왼쪽에 위치한다.
- 루트(Root) 노드를 기준으로 큰 값은 오른쪽에 위치하게 된다.
- 모든 원소들의 값은 중복되어서는 안 된다.
이진 검색 트리 삽입 연산
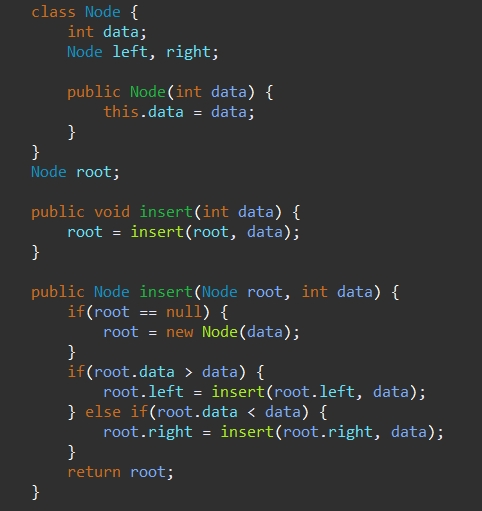
- root 노드가 null일 경우 노드를 생성하여 루트에 삽입
- 삽입할 data값이 root의 data값보다 작을 경우, 왼쪽 노드에 data를 삽입
- 삽입할 data값이 root의 data값보다 클 경우, 오른쪽 노드에 data를 삽입
이진 검색 트리 검색
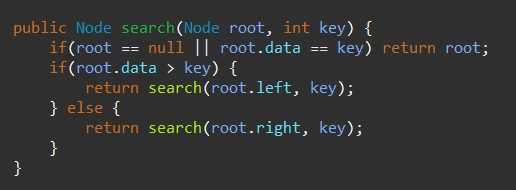
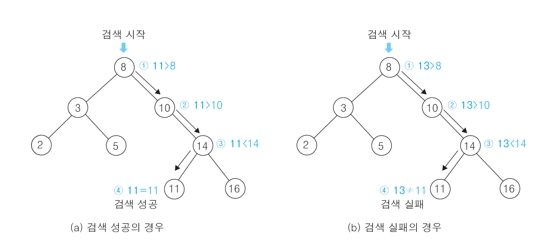
- 찾고자 하는 값과 노드의 key값이 같게 되면 검색 성공
- 찾고자 하는 값이 노드의 key값보다 작으면 왼쪽 노드를 기준으로 찾을 때까지 재귀함수를 통해 반복
- 찾고자 하는 값이 노드의 key값보다 크면 오른쪽 노드를 기준으로 찾을 때까지 재귀함수를 통해 반복
이진 검색 트리 삭제 연산
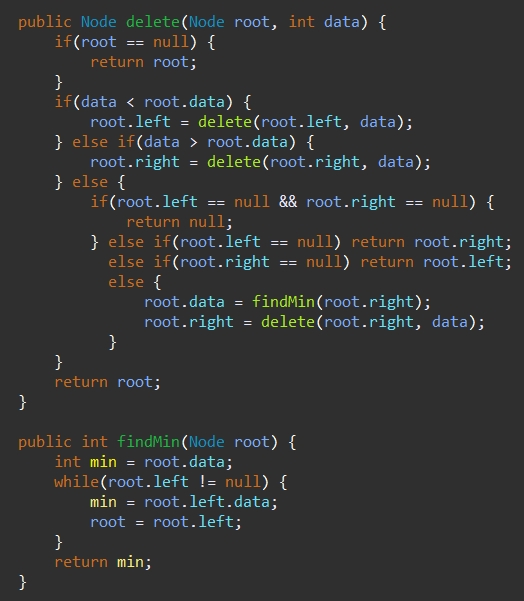
- no child : 부모의 링크를 끊는다.
- one child : 부모의 링크를 조정한다.
- two child : 해당 노드 삭제, 왼쪽(max), 오른쪽(min)으로 수정
- 구현 코드
public class BSTSearch {
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node root;
public void insert(int data) {
root = insert(root, data);
}
public Node insert(Node root, int data) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(data);
return root;
}
if (data < root.data) {
root.left = insert(root.left, data);
} else if (data > root.data) {
root.right = insert(root.right, data);
}
return root;
}
public void inorder() { // 순서대로 찍는다. 왼쪽 > 가운데 > 오른쪽
inorder(root);
System.out.println();
}
public void inorder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
inorder(root.right);
}
}
//검색
public Node search(Node root, int key) {
if (root == null || root.data == key)
return root;
if (root.data > key) {
return search(root.left, key);
} else {
return search(root.right, key);
}
}
public Node delete(Node root, int data) {
if(root == null) return root;
if(data < root.data) {
root.left = delete(root.left, data);
} else if(data > root.data) {
root.right = delete(root.right, data);
} else { //대상을 찾았을 경우
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) return null;
else if(root.left == null) return root.right;
else if(root.right == null) return root.left;
else {
root.data = findMin(root.right);
root.right = delete(root.right, root.data);
}
}
return root;
}
public int findMin(Node root) {
int min = root.data;
while(root.left != null) {
min = root.left.data;
root = root.left;
}
return min;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BSTSearch tree = new BSTSearch();
tree.insert(4);
tree.insert(2);
tree.insert(1);
tree.insert(3);
tree.insert(6);
tree.insert(5);
tree.insert(7);
tree.inorder();
tree.delete(tree.root, 7);
tree.delete(tree.root, 6);
tree.delete(tree.root, 2);
tree.inorder();
Node node = tree.search(tree.root, 5);
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("찾을 수 없습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println(node.data);
}
}
}
'Algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 깊이 우선 탐색(DFS) (0) | 2020.08.01 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 자바 Queue 정리 (0) | 2020.07.30 |
| [자료구조] 자바 Stack 정리 (0) | 2020.07.29 |
| [정렬] 버블정렬(Bubble sort) (0) | 2020.07.19 |
| [정렬] 선택정렬 (Selection sort) (0) | 2020.07.18 |



